Top 20 HR Influencers Shaping Digital HR Transformation in India
India’s talent or human resources is powering a $5T digital economy. To harness this opportunity, organizations must become AI-ready, and this critical shift is being driven by HR and L&D leaders who are at the forefront of preparing people for an AI-first future.
How HR Influencers Are Accelerating India’s AI-Ready Workforce
These HR and L&D leaders occupy a pivotal role because they influence how organizations reskill employees, cultivate agile mindsets, and embed AI fluency into everyday work. They are shaping new talent strategies, pioneering innovative learning models, and fostering cultures that embrace continuous transformation.
What sets these leaders apart is their commitment to testing emerging approaches, sharing knowledge openly, and leading change with real-world impact. They act as catalysts and role models, driving adoption of AI-powered talent development through bold vision and practical execution.
This curated list highlights 20 influential CHROs, L&D pioneers, and HR tech advocates who are leading India’s workforce transformation in 2026. Following their journeys offers valuable lessons on navigating the complexities of AI readiness while empowering people to thrive.
Below is an overview of who they are, how they are influencing the future of work, and why organizations should look to them as inspiration for their own AI and talent transformation strategies.
India’s Top 20 HR Tech Influencers Shaping the Future of Work
1. Harjeet Khanduja
Reliance Jio | Sr. VP HR
Harjeet Khanduja is an author of seven books on HR and leadership, a TEDx speaker, and holds multiple patents in HR technology. He has been honored with awards such as the Economic Times Top 20 HR Influencers in 2023, named among the Top 200 Global Leadership Voices in 2022, and featured among Thinkers360’s Top 50 Global Thought Leaders on HR.

2. Prabir Jha
Prabir Jha People Advisory | Founder & CEO
Prabir Jha is a seasoned HR influencer on LinkedIn, TEDx speaker, and active commentator with diverse industry experience, having served as CHRO for two New York Stock Exchange-listed companies and two Fortune 500 firms.
3. Shaji Mathew
Infosys | CHRO
As CHRO of Infosys and Group companies, leads global HR strategy, leadership development, and education/training for 250K+ employees while serving as Trustee of Infosys Foundation driving impactful CSR initiatives. Governance Board member at IIIT Bangalore and CII National Committee on Leadership & HR.
4. Thirumala Arohi
Cognizant | Chief Learning Officer
Heads the world’s largest corporate university serving 250K+ employees. Arohi brings over three decades of experience and is known for building scalable learning ecosystems and driving innovation in digital education.
5. Saswati Sinha
Trinity Life Sciences | Head of People (India)
Seasoned HR professional who drives healthcare sector talent excellence strategies. She is recognized consecutively as Top 100/101 HR Minds in India (World HRD Congress 2018-2019) and Asia’s Top 100 Power Leaders (2022), among other prestigious accolades.
6. Rajiv Naithani
Persistent Systems | Chief People Officer
Visionary HR leader driving organizational transformation through “Employee First” strategies. Youngest Country/Region/Global HR Head at GlobalLogic, Dassault Systèmes, and Infogain; recipient of CEO Awards and Asia’s Best Employer Brands “Young HR Professional of the Year.”
7. Vineet Nayar
Sampark Foundation | Founder & CEO
Management visionary who transformed HCL from $0.7B to $4.7B global tech services leader. Author of bestselling Harvard Business Press book; Fortune’s first “Executive Dream Team” 2012 and Thinkers 50 list member; Forbes’ 48 Heroes of Philanthropy 2016 for Sampark Foundation’s education innovation impacting millions.
8. Richard Lobo
Tech Mahindra | Chief People Officer
Global HR leader with 25+ years transforming people functions and strategically aligning talent to drive business growth in complex environments. Recognized as Economic Times HR Leader of 2023. Active CII/NASSCOM contributor and mentor nurturing future leaders through teaching at top management institutes.
9. Ankit Jhamb
Grant Thornton Bharat LLP | Chief Learning Officer
Chief Learning with 17 years of experience, delivering business impact. TEDx speaker, certified coach, clinical hypnotherapist, and author of 10 books on personal/professional growth.
10. Prasanna Shivakamat
Atos | Group Head L&D
Prasanna transforms global tech services learning ecosystems. He is also a “Future Learning Leader” 2024 awardee pioneering digital reskilling.
11. Dr. Ankita Singh
CIGNEX | Chief People Officer
Ankita Singh leads CIGNEX Datamatics’ HR, Administration, Travel, and Resource Management teams, driving a performance-driven culture that earned multiple “Great Place to Work” certifications. She is recognized with Forbes India’s Top 100 Great People Managers and numerous accolades including CHRO of the Year (2017-2020) and Femina’s Women Personality of the Year (2018-2019).
12. Salil Chinchore
ElasticRun | CHRO
Featured in “HR 100: People Leaders Shaping the Future of Startups,” Salil brings 28 years of HR and general management experience across organization strategy, talent/leadership development, employee engagement, global HR, labor relations, and M&A. Consistently high performer leading diverse HR functions in fast-paced unicorn environments, creating thriving workplaces that drive growth and culture.
13. Dr. Amit Das, Ph.D.
Bennett Coleman & Co. Ltd. (Times Group) | Director HR & CHRO
Strategic HR leader with 35+ years across MNCs like Tata Motors, Vodafone, Britannia, Taj Hotels, and Reliance Group, spanning diverse sectors and global geographies. Board/Governing Council member for corporate and educational entities; key Think Tank advisor to Central/State Government ministries driving transformational growth.
14. Dipti Madan
Newage Software & Solutions | HR Director
An HR Director who oversees Quality and HR functions, with Lean Six Sigma Black Belt, focused on process excellence and automation. Exemplifies the “never-give-up” mindset and recognized with The Global Excellence Awards – Edition 09.
15. Achal Khanna
SHRM India, APAC & MENA | CEO
Dynamic leader with 30+ years across diverse industries, serving as CEO of SHRM for India, APAC, and MENA region, driving global HR transformation and inclusive workplaces. Recipient of prestigious “Best Women Executive in India” award. She is a board member at Ascentios Advisors and MPS Limited, championing women’s empowerment, company culture, and leadership development.
16. Arun Kakatkar
Microsoft | Human Resources Leader
Seasoned HR leader driving business strategy, culture, and organization capability at Microsoft India. Expert in leadership development, high-performing teams, and strategic change management across global tech and manufacturing sectors.
17. Lakshmi Chandrasekharan
Accenture India | CHRO
With 20+ years in HR leadership roles at Accenture and prior experience at iGate and Nestle, Lakshmi champions equal, empowering cultures and mentors diverse young talent, especially women. Lakshmi co-chairs FICCI’s HR & Skills Committee and serves on XLRI’s advisory board for Gender Equality & Inclusive Leadership.
18. Thirukumaran R
Nokia | Talent Attraction Leader
Influential HR leader at Nokia with expertise in workforce trends, policy, and business alignment, fostering integrity-based employee-organization relationships. Recognized as Economic Times Top 20 HR Influencers 2020, official SHRM Influencer, People Matters Authors Squad, rise.global Top 100 Global HR Influencer, and Glassdoor Top Contributor at Employer Branding Summit 2015.
19. Saurabh Govil
Wipro | President & CHRO
Saurabh Govil leads Wipro’s entire HR function, including talent acquisition, engagement, and learning & development programs. With over two decades in HR, he has driven key people, processes, and structural initiatives fueling Wipro’s growth. He serves on SHRM India’s advisory board, speaks regularly at NASSCOM HR summits, and contributes to NHRDN’s journal.
20. Piyush Mehta
Genpact | CHRO & Country Manager India
Piyush Mehta leads global HR for Genpact, driving talent strategy, employer branding, and Data-Tech-AI transformation while representing the company with key India stakeholders. Key leadership council member with 20+ years of experience. NASSCOM Executive Council member and SHRM global certification commissioner.
Why These HR Influencers Matter for India’s Future
These 20 popular HR voices represent the future of India’s talent transformation landscape. Their pioneering work across technology, pharma, manufacturing, and services is driving scalable, AI-powered workforce strategies crucial for succeeding in today’s digital economy.
Explore more insights from India’s HR leaders in our in-depth analysis. Check out this blog.
👉 https://www.tekstac.com/hr-insights-from-leaders/
What are Skill Insights? How They Shape Tekstac Client Spotlights
While organizations invest heavily in learning programs, many still struggle to answer a critical question: what skills do we truly have, and where are the gaps?
That’s where Skill Insights come in.
Skill Insights go beyond traditional learning analytics. They offer a real-time, data-driven view of workforce capabilities, helping organizations identify strengths and make skill gaps analysis. Not only that, but they also empower leaders to make informed decisions about training investments, workforce planning, and business readiness.
At Tekstac, we’ve reimagined how Skill Insights are built and used.
What Are Skill Insights?
Skill Insights are comprehensive, analytics-based assessments of employees’ skills. They combine quantitative data (like assessments, certifications, and performance metrics) with qualitative inputs (like feedback and project outcomes) to give organizations a clear, holistic view of workforce capabilities.
Unlike conventional skill mapping, which often relies on self-reported data, Skill Insights are dynamic and validated through continuous learning and performance tracking.
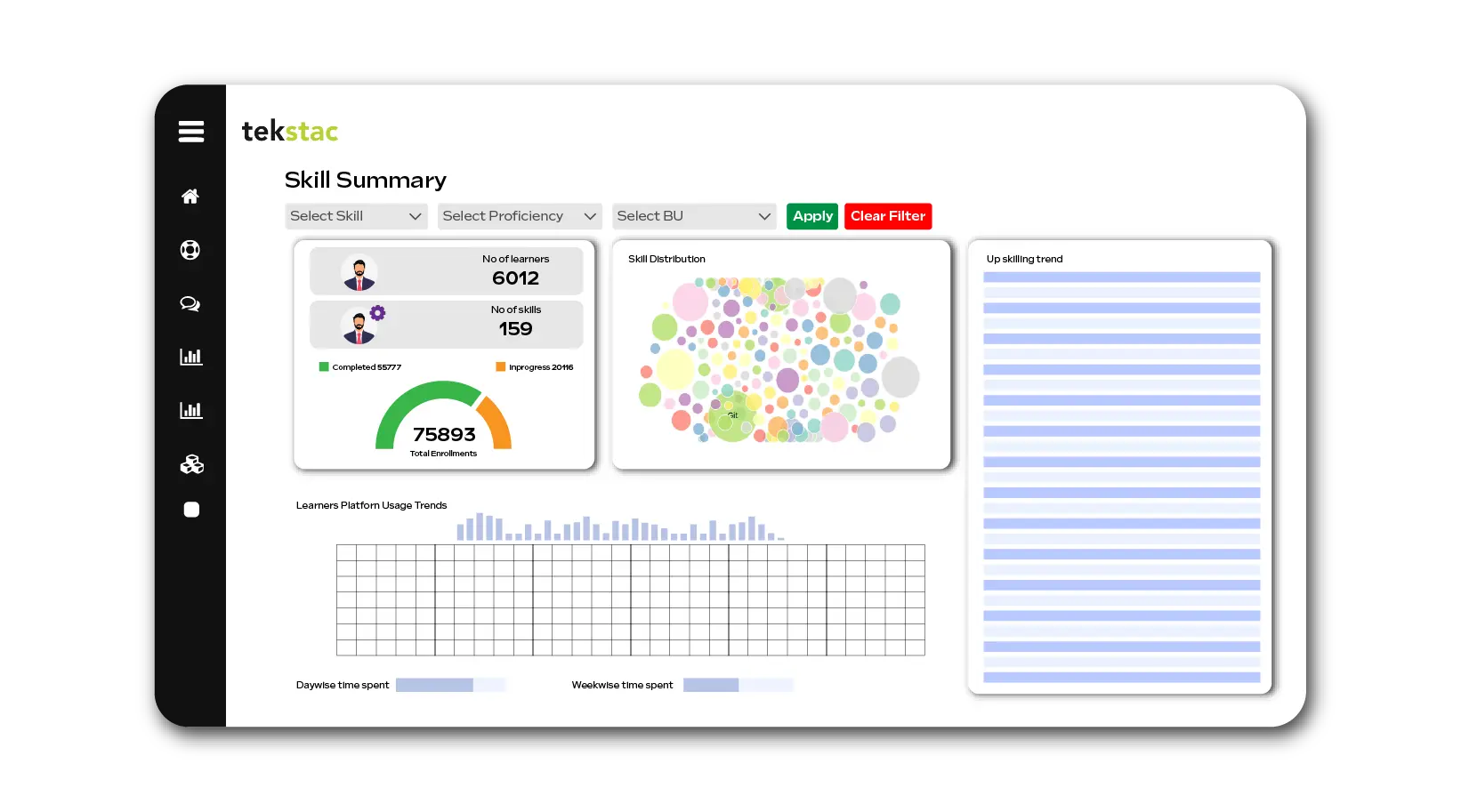
With Skill Insights, leaders can:
- Understand their workforce’s current skill landscape
- Identify skill gaps across roles and business units
- Align training programs to organizational goals
- Predict future capability needs
- Track how learning translates into real-world performance
In short, Skill Insights turn learning into measurable business value.
Tekstac’s Unique Approach to Building Skill Insights
Tekstac’s vision is to create a dynamic and evolving database of skill profiles, what we call the SkillTag.
A SkillTag isn’t static; it evolves alongside an individual’s professional journey. Each SkillTag reflects a learner’s real-time growth, capturing how skills are acquired, applied, and advanced within the organization.
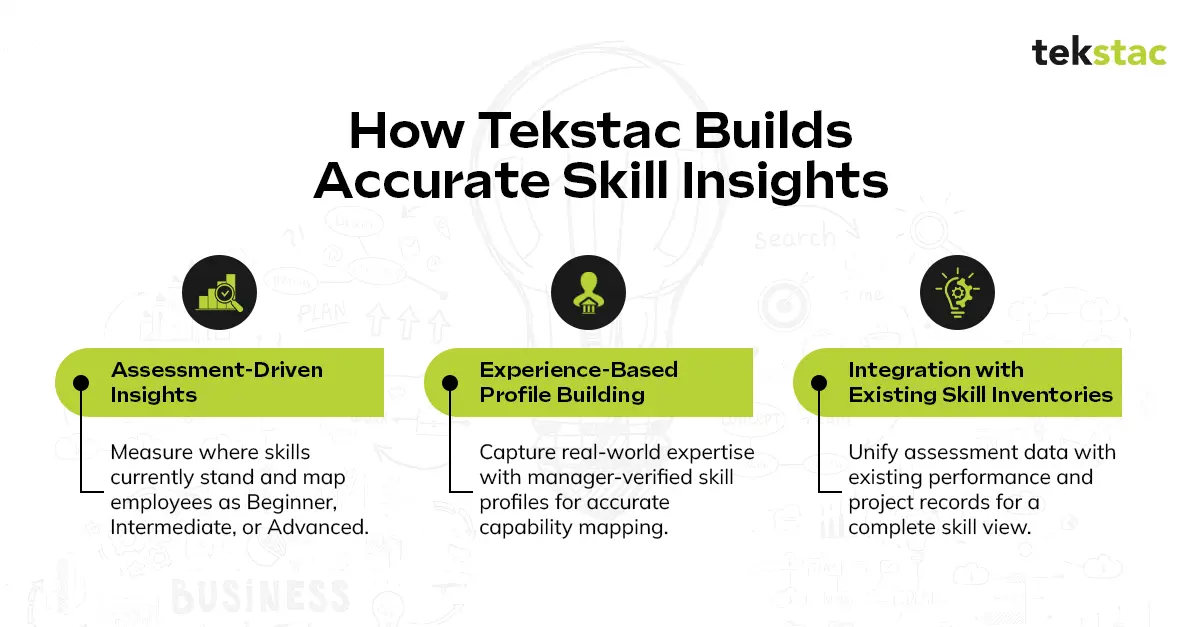
Our Skill Insights framework combines three powerful methods:
1. Assessment-Driven Insights
Tekstac’s pre-assessment engine allows employees to gauge their proficiency levels across specific skills. The results categorize individuals as beginner, intermediate, or advanced, providing a clear foundation for the organization’s skill inventory.
2. Experience-Based Profile Building
Not all expertise can be measured through assessments alone. For experienced professionals, Tekstac enables the creation of skill profiles based on self-declared data, verified by managers or cross-referenced with organizational records. This ensures that practical experience and institutional knowledge are accurately represented.
3. Integration with Existing Skill Inventories
Many organizations already maintain some level of skill tracking through performance reviews or project data. Tekstac integrates this information, enriching it with insights from our assessments and learning modules.
From Data to Direction: Turning Skill Insights into Action
Skill Insights are only valuable when they drive measurable action. Tekstac’s platform makes this possible through a suite of analytics and visualization tools:
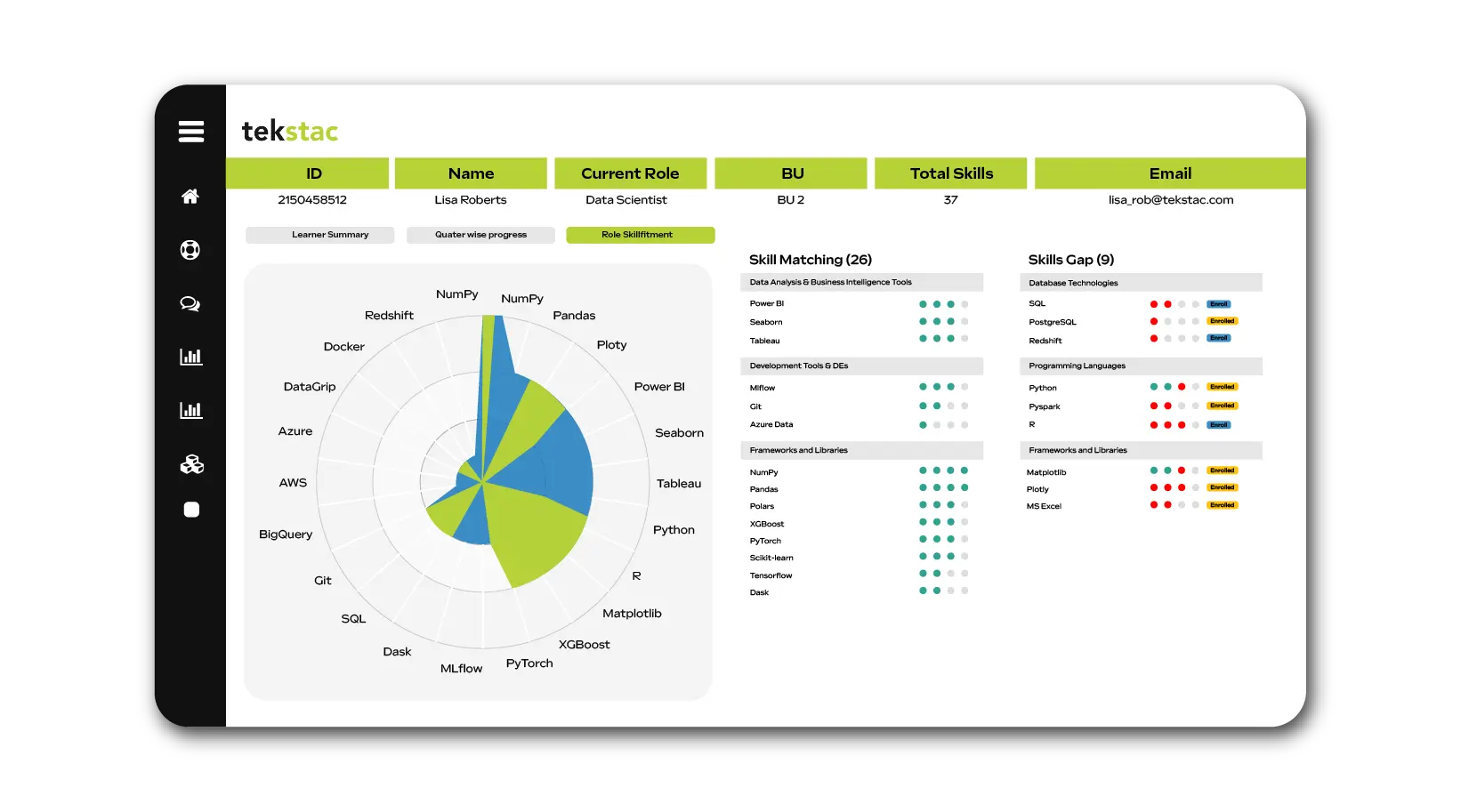
- Growth Path Analyzer helps employees identify skill gaps for internal mobility and choose between organization-mandated or aspirational growth paths.
- Skill Inventory & Analytics tracks progress, identifies gaps, and helps optimize workforce development.
- Predictive Analytics enables program planning, skill availability forecasting, and proactive learning interventions.
- Role vs. Skill Gap Analysis ensures employees are matched to the right roles and receive the right upskilling recommendations.
- Reports & Dashboards provide visibility for leadership, operations, trainers, and learners, creating a shared language of skill growth across the enterprise.
As employees grow, AI continuously updates their SkillTags, detecting evolving skills from day-to-day activities, keeping profiles current.
Tekstac Client Spotlights
The true power of Skill Insights comes to life through Tekstac’s Client Spotlights. Here is a glimpse at our client success stories in L&D.
Case Study 1: A Fortune 500 Global IT Consulting Leader
Challenge:
The client, with a 300,000+ global workforce, wanted to accelerate workforce mobility and efficiency through lateral training programs. But they faced multiple hurdles: limited visibility into skill gaps, generic learning programs, and an inability to link training efforts with performance outcomes.
Tekstac’s Solution:
- Role-Based Personalized Learning Paths: Employees received customized learning journeys based on auto-evaluated skill assessments.
- Competency Mapping & Analytics: Real-time insights helped managers identify high-potential employees ready for new roles.
- Auto-Evaluated Assessments: Knowledge retention and role readiness were validated objectively.
- Robust Reporting Dashboards: Leadership gained visibility into skill progress, training ROI, and workforce readiness.
Case Study 2: Fortune 500, Big Four Company
“What sets Tekstac apart is not only its technical superiority but also its people. Their commitment to service excellence is exemplary. We now rely on Tekstac to train over 5,000 students across diverse disciplines.” — Senior Manager, L&D, Fortune 500, Big Four Company
Through Skill Insights Analytics, the organization gained visibility into learning behavior, engagement trends, and skill adoption rates.
Case Study 3: US-based Fortune 500 Services-based Company
“The analytics features on the Tekstac platform have helped us understand learning patterns and plan the right interventions. Over the last three years, we’ve had 100% platform availability — zero downtime.” — VP, Learning and Knowledge Management, US-based Fortune 500 Services-based Company
With Tekstac’s data-driven learning insights, Accenture achieved consistent engagement, smarter intervention planning, and measurable improvements in skill adoption.
Case Study 4: Gramener
“Our graduates underwent a five-week data science program on Tekstac. The platform’s auto-evaluated labs and assessments ensured better than expected ROI. The support from Tekstac’s team was top-notch.” —Head of ESG and Analytics, Gramener
Gramener leveraged Tekstac’s Skill Insights to streamline onboarding, strengthen analytics capability, and align learning outcomes with project demands — accelerating readiness for client delivery.
Why Skill Insights Matter More Than Ever
The future of work demands agility. Skills are becoming obsolete in a few years, and organizations can no longer rely on static training models. They give leaders confidence that they have the right capabilities to execute technology strategy. Teams can benchmark expertise across roles, accelerate release cycles, and build reliable, secure products.
By integrating Skill Insights Analytics with AI-driven assessments and real-time dashboards, Tekstac makes it possible to put the right people on the right projects.
Key Takeaways on Skill Insights
At Tekstac, we believe learning should be intelligent, adaptive, and human-centered. Our Skill Insights feature combines the precision of AI with the depth of human expertise.
And through our Client Spotlights, we continue to showcase how enterprises worldwide are using Tekstac to bridge skill gaps, unlock potential, and build a truly future-ready workforce.
Request Your Free Demo Now and discover how your teams can optimize workforce development.
Building Tech Talent Pipelines: Inside Tekstac’s Learning Platform
When a critical tech project came up, one of our client organizations was confident their team could deliver. The talent was experienced, the processes were in place, and the skills seemed sufficient.
But when the project required newer AI, cloud, and data integration capabilities, performance dropped. The team needed immediate reskilling—and external hiring became the only short-term fix.
This is not an isolated story. It’s a reminder that tech capability doesn’t scale on its own. In reality, future-ready talent isn’t hired—it’s built through deliberate design. That design is what we call a tech talent pipeline.
Why Tech Talent Pipelines Have Become a Business Moat
In today’s fast-changing digital economy, continuous upskilling has become the backbone of enterprise competitiveness.
Technology evolves faster than job roles, and without a structured system to build capabilities, even strong teams risk obsolescence.
While most enterprises recognize this, many still rely on ad-hoc training. What’s needed instead is a data-driven, AI-enabled talent framework that continuously builds, tracks, and sustains skill readiness across functions and technologies.
At Tekstac, we’ve seen this gap firsthand. Traditional training programs can’t keep pace with new tech stacks, agile workflows, and the speed of AI adoption.
That’s where Tekstac’s AI-driven learning platform transforms how organizations develop tech capability—aligning skill development with measurable performance outcomes.
How Tekstac Redefines Tech Capability Building
Tekstac’s learning ecosystem is built around one idea: Tech readiness should be business-aligned, continuous, and measurable.
Our platform helps enterprises operationalize tech talent pipelines that move beyond certifications and one-time bootcamps—into a system of lifelong learning and performance-linked growth.
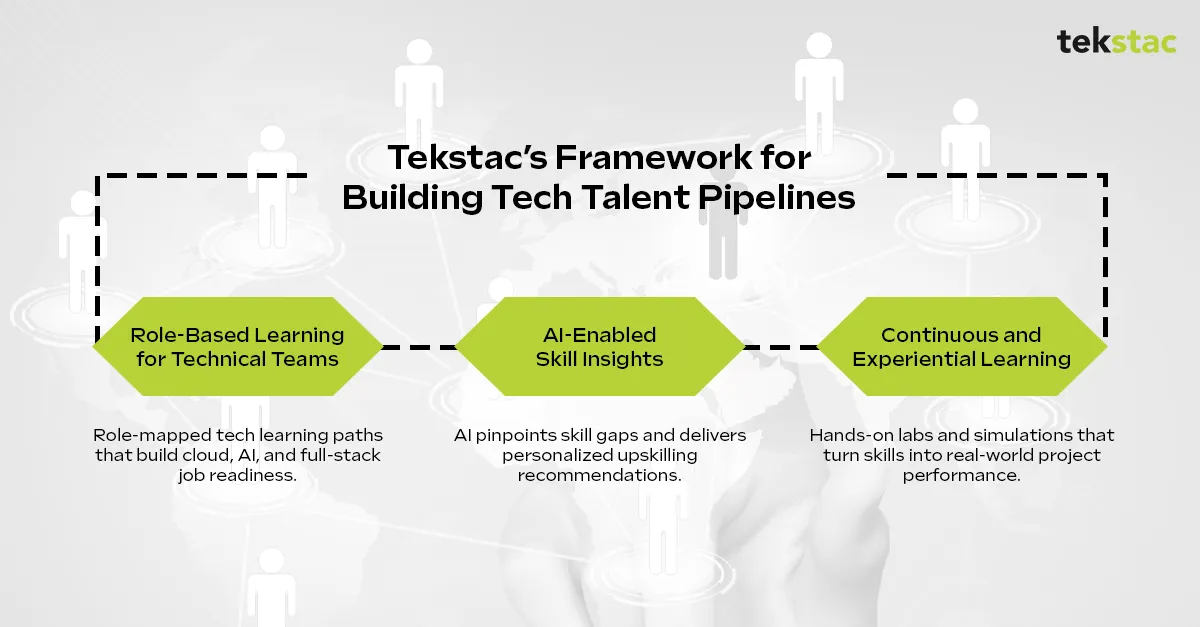
Here’s how it works:
1. Role-Based Learning for Technical Teams
Tekstac’s role-based learning structure maps every module to real-world project needs—whether that’s cloud migration, full-stack development, or AI implementation.
Each pathway blends course modules with hands-on coding labs, simulations, and project assessments, building real world application ready, deep technical mastery for each role.
2. AI-Enabled Skill Insights
AI in talent development is no longer a nice-to-have—it’s mission-critical.
Tekstac uses AI-powered analytics to identify skill gaps, benchmark capabilities, and recommend personalized learning paths.
This approach helps enterprises proactively develop internal talent—reducing dependency on external hiring and ensuring readiness for emerging technologies.
3. Continuous and Experiential Learning
Technical skills evolve every quarter. Tekstac integrates experiential learning that helps teams apply what they learn immediately in the flow of work.
This gives L&D and business leaders data-backed visibility into skill progress, role readiness, and workforce ROI.
The Cost of Inaction: Why External Hiring Shouldn’t be the only Answer
When new technology initiatives arise, organizations often default to hiring externally. But a recent Forbes research report shows that 58% of companies are now focused on building a culture of continuous learning, and 69% believe every employee needs technical upskilling opportunities.
External hires, meanwhile, often struggle with culture fit, take longer to reach peak productivity, and increase cost per hire.
Building a tech talent pipeline helps organizations develop talent that already understands the systems, culture, and clients they serve.
How Tekstac Helps Build Tech Talent Pipelines
At Tekstac, tech learning isn’t just course-driven—it’s experience-led. Each program simulates real-world engineering challenges.
Learners progress through interactive, structured modules, hands-on labs, and instant feedback for performance improvement.
Key platform highlights:
- 500+ customizable, role-aligned tech learning paths
- Auto-evaluated coding labs with instant grading
- Real-time dashboards for progress and proficiency tracking
- Gamified XP points, badges, and leaderboards
- Mentor marketplace with rubric-based evaluations
By the end of each program, learners earn a SkillTag—a verified record of competencies that reflects job readiness and tech mastery.
Future-Proofing Talent in the Age of AI
Tech skills now have shorter half-lives than ever before.
In the AI era, the future workforce must be capable of re-skilling, adapting, and integrating new technologies continuously.
Skill gaps don’t appear overnight—they grow silently when learning is reactive. A well-structured tech talent pipeline changes that narrative. It ensures readiness at every level, continuity in every transformation, and a workforce that grows as fast as technology does.
Tekstac’s Learning Platform helps organizations move from reactive hiring to proactive capability design—enabling HR and L&D leaders to build, measure, and sustain the tech talent their businesses need for the future.
Book a Tekstac demo today and start building your tech talent pipeline.
Top 7 Learning and Development (L&D) Events in India for 2026
2026 is almost here, and the L&D function is gearing up for another year of transformation. From AI-powered upskilling to skills-first workforce planning, learning and development events are becoming the spaces where our industry resets, rethinks, and realigns.
Across India, several L&D events in India are lined up for 2026, bringing together practical case studies, future-skills frameworks, and discussions on talent transformation in GenAI era. Whether your focus is immersive learning or building employee learning programs at scale, these events offer high-value insights for every stage of growth.
Here are seven high-impact workplace learning conferences in India you should consider attending. Each one offers something unique, strategy playbooks, peer conversations, tech showcases, and fresh inspiration for your next phase of talent transformation.
Key Learning and Development Events for 2026
1. 17th L&D & Talent Management India Summit & Awards 2026
Date: 28 January 2026
Venue: Radisson Blu Mumbai International Airport
Visit: https://lndleadershipsummit.com/
Synopsis:
A long-standing industry favorite, this summit brings together CHROs, CLOs, and talent leaders to decode what’s next for capability building. Expect conversations around leadership transformation, digital academies, skill mobility, and scaling training and development events across enterprise teams.
2. The 22nd Edition Future of Learning & Development Summit & Awards 2026
Date: 13 February 2026
Venue: Mumbai
Visit: https://futurelnd.com/
Synopsis:
With the theme of Engage – Empower – Elevate, this conference offers deep dives into immersive learning, hybrid architectures, and AI-enabled skilling. It’s a must-attend for teams redesigning employee learning programs for long-term impact and agility.
3. Asia L&D & Employer Branding Conference & Awards – 2nd Edition
Date: 13 February 2026
Venue: Hotel The Den, Bengaluru
Visit: https://www.ibcinfo.com/events-details/event/asia-ld-employer-branding-conference-awards-2nd-edition/
Synopsis:
This event combines L&D strategy with culture and communication. Expect discussions on learning experience design, reskilling frameworks, employee value propositions, and capability building. Emphasizing strong identity and talent transformation in GenAI era, this event recognizes a crucial theme across skill development conferences.
4. The Economic Times NexTech HR Summit 2026
Date:18–19 February 2026
Venue: The Leela Ambience, Gurugram
Visit: https://hr.economictimes.indiatimes.com/nextech
Synopsis:
Themed Minds & Machines: Shaping Tomorrow, NexTech explores how India can advance as a global talent capital. With its strong focus on automation, workforce readiness, and scalable skilling, it’s a core event for organizations investing in future skills summits and digital transformation.
5. The Best Firm Summit 2026
Theme: Reimagining the Future of Human Capital in the Era of AI
Date: 17 April 2026
Venue: Radisson Blu, Outer Ring Road, Bengaluru
Visit: https://summit.bestfirm.aim.media/
Synopsis:
Designed for leaders building AI-driven workplaces, this summit covers automation-integrated talent ecosystems, capability academies, and intelligence-driven workforce planning. Perfect for teams working at the intersection of AI and enterprise learning.
6. People Matters TechHR India 2026
Date: 6–7 August 2026
Venue: Yashobhoomi Convention Centre, New Delhi
Visit: https://india.techhrconference.com/
Synopsis:
Asia’s largest HR & work-tech conference, TechHR is one of the prestigious learning events where L&D meets the future of work. From behavioral analytics to next-gen platforms and capability intelligence systems, this is the place for organizations prioritizing upskilling and reskilling and talent transformation in GenAI.
7. SHRM India Annual Conference & Expo 2026
Date: 26–27 November 2026
Venue: Taj Palace, New Delhi
Visit: https://www.shrmconference.org/iac
Synopsis:
One of India’s most influential HR and L&D industry events, SHRMIAC brings global experts, masterclasses, and research-backed insights. Expect future-skills playbooks, capability frameworks, GenAI strategies, and case studies from high-performing enterprises.
Why These Learning Events Matter in 2026
Across all seven learning and development events, a few powerful themes consistently emerge:

1. AI-Accelerated L&D
GenAI is moving from pilots to enterprise-scale adoption. Learning teams are overhauling content operations, personalization engines, and taxonomies using AI.
2. Skills Over Roles
Organizations are shifting to agile skill architectures, prioritizing skills mapping, adjacent skills, skills-based career pathing, and internal mobility.
3. Experience-Led Learning
Simulations, microlearning, practice labs, and mentor interventions drive higher retention and provide real-world application-based learning.
4. Measurement & ROI
L&D is now directly tied to business outcomes. Leaders want clearer impacts such as faster deployment readiness, reduced cost of hiring, better build vs buy vs borrow talent decisions, skills insights to build proactive talent pipeline that helps in measurable ROI.
5. People-Centric Tech Adoption
As tool fatigue rises, L&D must re-design people-first systems that feel simple, intuitive, and human by default. A powerful theme that propagates talent transformation in the GenAI era.
How Tekstac Engages in These Learning Events
Throughout 2026, Tekstac will actively participate in these learning and development events, conducting roundtables, working on new research, unveiling capability frameworks, and hosting demos. These interactions help us stay deeply connected to the evolving challenges of learning teams, enabling us to co-create solutions with the industry.
Accelerating Talent Transformation in GenAI Through Learning and Development Events
Learning and Development Events are no longer passive industry gatherings; they’re catalysts for transformation, capability building, and meaningful collaboration. As 2026 brings a new wave of innovation, these seven conferences offer the insights, networks, and frameworks to help L&D teams stay ahead of rapid change.
Whether you’re refining your skilling strategy, rethinking systems, or preparing your workforce for the future, these learning events offer everything you need to accelerate talent transformation in the GenAI era.
How Tekstac Helps L&D Managers Hit Business KPIs Faster
Less than one in three skilling programs today directly impacts business KPIs. The rest? They keep churning out content. It’s no wonder that when L&D functions like a content factory, the business treats learning as optional.
To lead, L&D must become the capability engine: strategic and data driven.
While most of them still measure the traditional surface-level metrics such as:
- Completion rates
- Assessment scores
- Attendance numbers
These numbers still don’t answer the most important question: Did skill development actually change performance?
So how can L&D teams boost business KPIs efficiently?
That’s where platforms like Tekstac come into picture. See how Tekstac helps organizations in reaching learning and development KPIs.
Why Traditional L&D Metrics fail to deliver business KPIs?
Metrics like the number of hours trained or course completions are easy to measure but fail to capture the real training ROI measurement.
Let’s see why.
For instance:
- A team may complete a leadership program, but if decision-making doesn’t improve, is it worth the time?
- Employees may score high on assessments, but if sales numbers don’t change, did the learning truly stick?
L&D should replace activity tracking with meaningful skills gap analysis.
It means mapping current skills to business goals, finding critical gaps, and creating focused upskilling programs to close them.
This shifts L&D from spotting problems to solving them, building the right skills, in the right people, at the right time.
What Defines L&D Business KPI?
L&D business KPIs help organizations move from measuring participation to measuring performance change. Remember to identify the right KPIs for your L&D.
The role of KPIs in L&D:
- Provide visibility into the effectiveness of training programs
- Show measurable ROI on learning investments
- Highlight both strengths and areas for improvement
- Align L&D with organizational strategy
Common Challenges in Measuring Learning & Development KPIs
Did you know? According to the LearnOps Industry Report (2024)33% of organizations don’t make L&D success measurements at all.
Listed below are some of the common challenges faced in tracking business KPIs
1. Proving ROI
One of the biggest hurdles for L&D managers is convincing leadership, that training delivers value. Without robust data, learning is seen as a “nice-to-have” rather than a strategic growth driver.
2. Relying Too Much on Easy-to-Track Metrics
Attendance numbers and retention rates are simple to report, but they don’t tell the full story. True measurement requires both quantitative data (scores, completions, proficiency levels) and qualitative insights (employee satisfaction, perceived value, behavioral change).
Overcoming these challenges requires the right employee performance KPIs, the right measurement approach, and the right technology.
Top 3 Ways Your Teams Can Consistently Hit Business KPIs
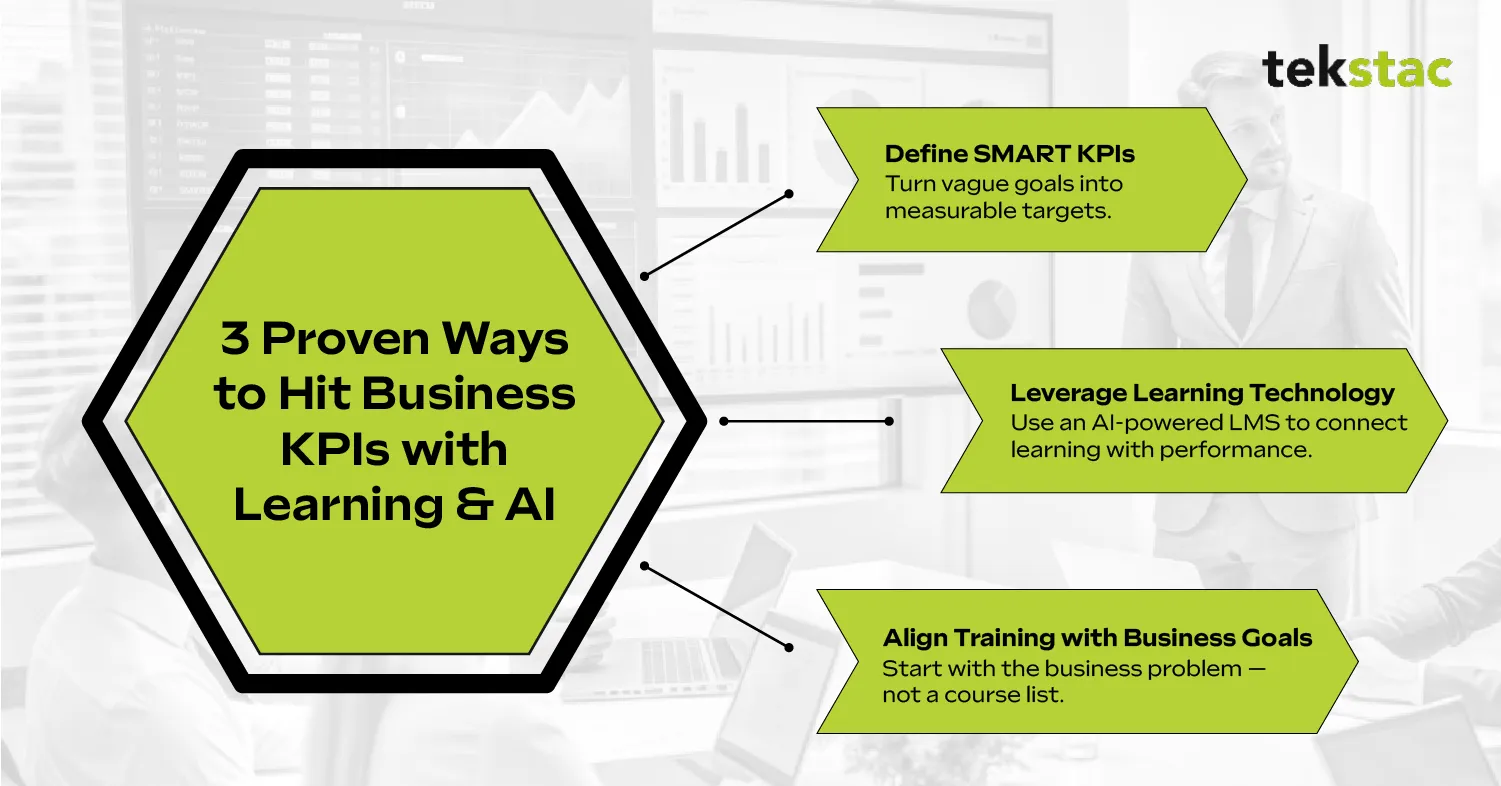
1. Define SMART KPIs
Instead of “Improve onboarding,” a SMART KPI would be “Reduce new hire ramp-up time by 20% within six months.”
2. Leverage Learning Technology
To truly measure and maximize the impact of learning, organizations need more than just training delivery—they need visibility, precision, and scalability. This is where an AI-powered Learning Management System (LMS) makes the difference and tracks upskilling impact on KPIs.
A AI-powered LMS can:
- Collect and centralize training data automatically
- Provide real-time dashboards on learner progress
- Personalize learning with skills gap analysis and adapting content
- Deliver insights instantly for leadership reporting
This shifts L&D from being reactive to proactively shaping workforce performance.
3. Align Training with Business Needs
Training should always start with a business problem, not a course catalog. Ask upfront:
- What challenge are we solving?
- Which learning and development KPIs will this training move?
- How will we measure success?
When learning initiatives are designed with these questions in mind, they not only engage employees but also prove their impact to stakeholders.
How Tekstac empowers you to track Business KPIs
Tekstac empowers L&D managers to link training directly to business performance through powerful learning analytics and management tools.
Why Tekstac:
- 360-degree platform with measurable ROI
- 500+ customizable, role-aligned learning paths
- Gamified experience with XP points, badges, and leaderboards
- AI-powered personalization & live dashboards
- Enterprise-grade security & compliance
- Data-driven skills insights
- Dual-layered assessments (auto + video with AI proctoring)
Enhanced learning experience with Tekstac
Beyond L&D success measurement, Tekstac powers learning delivery with:
- Personalized learning paths for every employee
- Mentor marketplace and virtual sessions
- Auto-evaluated practice labs
With 1 million+ professionals upskilled, 24 million+ learning hours, and enterprise clients like IBM, PwC, Capgemini, and Cognizant, Tekstac is proven at scale.
Where Skilling Meets Measurable Business KPIs
It’s time to stop tracking skill development for just the numbers. Instead of asking “Did employees finish the course?”, L&D managers must ask “What business KPI did this program improve?”
Track what matters and focus more on metrics stakeholders already value. Identify the employee performance KPIs before launching a program.
Need assistance with all this?
Tekstac transforms L&D from tracking hours and completions to driving measurable performance, stronger KPIs, and a future-ready workforce.
FAQs on business KPIs in L&D?
1. What are some examples of business KPI metrics in L&D?
Some examples for this include time to competency for new skills, utilizing acquired abilities in practical projects, Return on Learning Investment (ROLI).
2. What is KPI for L&D?
Learning and development KPIs are the steps you complete along the way in training. These KPIs for learning give you a meaningful way to quantify what good results are.
3. Which is a must track learning and development KPI?
One significant KPI one must track is training ROI, which measures the total value derived from training programs compared to their cost.
Tekstac vs Pluralsight: In-depth Feature and ROI Comparison
Imagine this: You’re leading L&D and need to decide how to spend your training budget. But you’re not sure how to measure if the programs are working. Sounds tricky, right? Actually, it’s not as hard as it seems. That’s where ROI comes in.
Every L&D leader today is looking at the cost v/s benefit of learning platforms to create a sustainable plan for the upcoming years.
Hence, choosing the right skilling platform that aligns with your goals becomes paramount. Here is a detailed ROI comparison between the two top-rated skilling platforms Tekstac and Pluralsight, to help you choose the right one.
ROI Comparison overview: Tekstac vs Pluralsight
When comparing Tekstac vs. Pluralsight, it’s crucial to understand their differences in content, certification, pricing, and learner focus. Both platforms cater to learners, but they differ in measuring corporate training ROI metrics.
Tekstac is an enterprise tech skilling platform with learning content, hands-on practice labs, assessments, ROI measurement dashboards and skills inventory tracking.
In contrast, Pluralsight specializes in 6,500+ tech-focused courses, tailored for IT professionals, developers, and engineers.
Who is Tekstac best for?
Tekstac is best suited for enterprises and learning leaders who need a 360-degree skilling platform to enable large-scale talent transformation. It is designed for organizations that want to upskill employees, accelerate role readiness, and track ROI on learning investments.
Who is Pluralsight best for?
Plural-sight is best for programmers, data scientists, data analysts, software engineers, computer engineers, IT professionals, and anyone in the tech workforce.
Here is the concise comparison table:
| Tekstac Features | Pluralsight Features |
|---|---|
The all-in-one platform features:
|
Prominent features include:
|
Tekstac vs Pluralsight: Which Platform Delivers Better ROI?
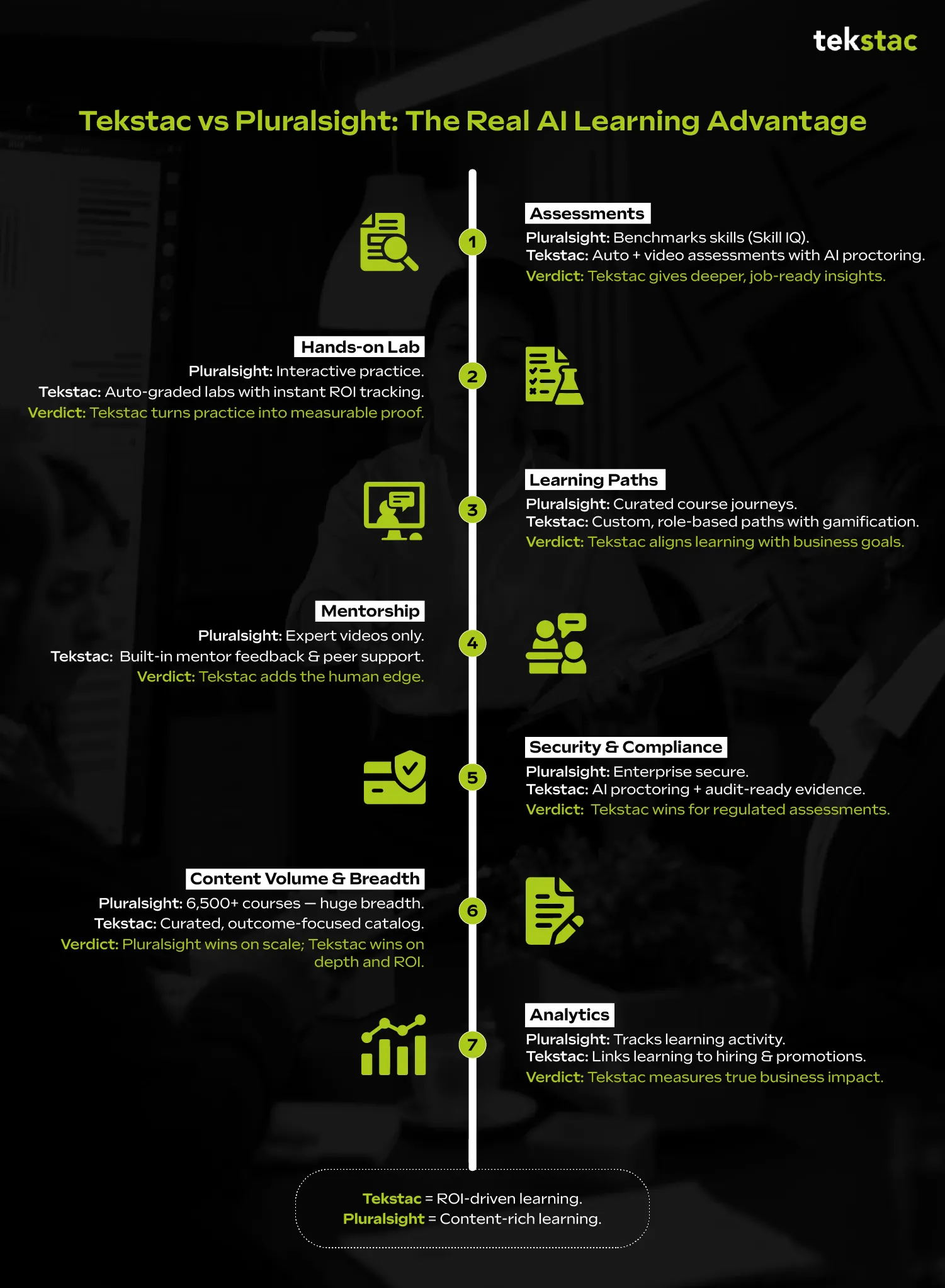
1. Assessments (What they measure and how they scale)
Pluralsight offers structured skill assessments (Skill IQ/Role IQ) to benchmark knowledge and recommend learning paths; these are useful for quickly measuring where a learner stands and for driving recommended content.
Tekstac, however, approaches assessment as a two-layered capability: instant, auto-evaluated assessments that gamify learning and deliver granular analytics, plus video assessments that evaluate communication, problem-framing, and applied thinking.
For companies doing a training ROI analysis, Tekstac provides a clearer picture of learner readiness and impact.
Verdict: Pluralsight’s Skill IQ provides a good benchmark, but Tekstac’s mix of auto-evaluated scoring, video responses, AI proctoring and mentor rubrics gives a richer, hire-ready assessment signal.
2. Hands-on labs and practice environments
Pluralsight has invested heavily in hands-on experiences: interactive labs, sandboxes, and in-browser code labs that let learners practice with cloud and desktop environments. These labs are great for isolated practice and platform familiarity.
Tekstac’s Auto-Evaluated Labs take it a step further, offering instant grading, personalized feedback, and corporate training ROI metrics by tracking skills acquisition in real time. Every submission is auto graded against test cases and performance metrics, with step-by-step personalized feedback and cohort analytics.
Tekstac’s labs are positioned as part of a continuous learning lifecycle, which reduces manual grading load and makes lab results usable as hiring or promotion evidence
Verdict: Pluralsight’s labs are excellent for practice; Tekstac’s auto-evaluation and integrated analytics convert practice into defensible proof of ability that clearly influences L&D ROI comparison.
3. Learning paths and personalization
Pluralsight’s core strength is a mature, searchable catalog and curated learning paths that guide learners from fundamentals to advanced topics, and the platform surfaces tailored recommendations based on assessment results.
Tekstac takes a different tack: instead of only offering pre-built paths, Tekstac promises 100% customizable, role-aligned learning journeys, LTI integration so existing third-party content can be unified, and gamified milestones to drive engagement. This ensures learning outcomes are directly tied to training ROI analysis.
Verdict: The combination of role mapping, gamification, and live dashboards means Tekstac’s paths can be tuned to business outcomes rather than just course completion.
4. Mentorship, human feedback and peer support
Pluralsight primarily scales through expert-authored video content and automated assessments; while it does offer guided learning experiences, direct mentoring/rubric-driven mentor review is not a core platform differentiator in the same way Tekstac makes mentoring part of the learning flow.
Tekstac’s Mentor Connect couples one-on-one and group mentoring, structured rubric feedback, and peer forums so learners get timely human guidance tied directly to assessment outputs. That human loop is especially valuable for borderline cases, candidate interviews, or nuanced technical topics where automated feedback can’t capture judgment or communication.
Verdict: Mentorship is blended into Tekstac’s product design, contributing to a higher Tekstac ROI, whereas Pluralsight focuses more on self-paced content and automated benchmarking.
5. Security, proctoring and enterprise compliance
Pluralsight markets enterprise features and governance for teams, and it’s widely used across companies for secure upskilling. But when it comes to integrated, assessment-level proctoring, that is not the headline differentiator Pluralsight promotes.
Tekstac’s Secure Proctoring Hub is designed natively into the assessment flow: AI monitors for impersonation, tab switching, unusual audio, produces confidence scores, and generates concise evidence packages for mentor review.
For regulated assessments, hiring decisions, or certification-grade testing, Tekstac’s approach reduces risk and administrative overhead while preserving learner experience. This level of compliance demonstrates the cost vs benefit of learning platforms in highly regulated environments.
Verdict: For high-stakes assessments and auditability, Tekstac’s native AI proctoring and reporting are stronger.
6. Content volume and course breadth
Here Pluralsight’s strength is indisputable: the platform advertises access to 6,500+ courses and thousands of hands-on labs and sandboxes, covering an exceptionally wide range of tech domains and vendors. For individual learners or teams who need breadth, Pluralsight’s catalogue is a compelling advantage.
Tekstac intentionally focuses on curated learning paths, role-aligned journeys and integrated assessment rather than quantity of discrete courses. If your priority is access to the largest possible library and immediate on-demand topic variety, Pluralsight gives more in volume
Verdict: Pluralsight has the upper hand here, when sheer scale and variety of course content are the deciding factor.
7. Analytics and business impact measurement
Pluralsight provides analytics and enterprise reporting (usage, skill gaps, role IQs) that help teams measure progress, but those analytics are principally consumption and assessment-level signals.
Tekstac layers skill-inventory analytics, cohort trend analysis, growth path analyzers, and ties assessment outputs (auto-graded labs + video rubrics + proctoring signals) to role readiness and hiring/upskilling decisions. The result is a product that not only shows who watched what, but shows who is demonstrably ready for a particular role or responsibility — and why.
Verdict: Tekstac’s analytics are explicitly designed to drive HR and L&D decisions (hiring, promotions, targeted reskilling), not just measure activity.
Why do companies check Tekstac vs Pluralsight ROI comparison chart?
ROI measurement is not a cakewalk in L&D. You need to answer a lot of questions. How do enhanced skills impact the organization’s financial strength? How does the company scale with other competitors in L&D ROI comparison? And so on.
Tekstac v/s Pluralsight ROI comparison will give insights on how they compare to one another in one of the most crucial metrics.
Pluralsight ROI metrics
Pluralsight training ROI analysis suggests that a 295% return on investment (ROI) over three years, with organizations seeing full payback in under six months, according to a Forrester Total Economic Impact™ study.
The ROI is driven by faster onboarding, improved employee retention, and accelerated product development, resulting in millions in productivity gains.
Tekstac ROI metrics
Unlike Pluralsight’s ROI comparison, Tekstac measures learning impact through skills outcomes, productivity, retention, and alignment with business goals.
Tekstac supported 110,000+ learners for one of its leading tech clients, improving talent identification, reducing hiring and training costs, accelerating productivity, boosting engagement, optimizing program management, and improving ROI.
Tekstac builds evolving, real-time skill profiles (“SkillTag”) per learner, integrating assessments and workplace data to inform talent strategies.
Final Thoughts: ROI Comparison and Key Takeaways
Both Pluralsight and Tekstac are top upskilling platforms—Pluralsight with expert-led learning, and Tekstac with real-world coding practice.
So, what’s right for you?
Pluralsight remains an industry leader for individuals and teams looking for an expansive, expertly authored course library with hands-on practice options. If your top priority is content breadth and immediate access to thousands of tech topics, Pluralsight is the safer pick.
But for organizations that is looking not just content but a comprehensive skill development platform that includes assessments to mean something (beyond “course complete”), want labs that act as verifiable proof of capability, require low-friction, enterprise-grade proctoring, and value human mentoring tied directly to analytics and role outcomes, Tekstac is the more outcome-oriented platform. Most importantly, Tekstac empowers the organization’s L&D teams with proven ROI that is clear and actionable.
Frequently Asked Questions on ROI Comparison
1. What is ROI in L&D?
ROI in Learning & Development is a way to measure how much value your organization gets from investing in employee training and development.
2. What factors influence L&D ROI comparison in companies?
Several factors impact L&D ROI comparison, including relevance of learning content, engagement levels, skill application on the job, and alignment with career progression or internal mobility goals. Platforms that integrate assessments, mentorship, and analytics, like Tekstac, provide richer insights for comparing ROI and making informed talent decisions, including promotions and lateral hiring.
3. How can organizations measure training ROI effectively?
Training ROI can be measured by tracking improvements in employee performance, time-to-competency, internal mobility readiness, and impact on business outcomes.
26 Strategic HR Insights from HR Tech Leaders for 2026
The HRTech 2026 conference, a gathering of global HR leaders and innovators, highlighted the trends, challenges, and breakthroughs shaping the future of work. We’ve compiled 26 key HR insights from sessions, panels, and conversations with leading voices.
These insights are organized into seven themes that capture the latest trends shaping HR. Let’s take a look.
7 Key Themes Shaping the Future of HR Insights
Theme 1: Talent Acquisition Reinvented
1. Candidate experience is now AI-enhanced
Discovery: Phenom and Paradox showcased GenAI-powered candidate communication—automated but personalized.
Why it matters: Candidate drop-offs happen when the process feels impersonal or slow. AI can help close that gap.
Action: Audit your candidate journey for speed, personalization, and human touch.
Quote: As Yvette Cameron (Oracle) noted, “The future of AI in enterprise software will become more conversational,” fundamentally changing how candidates and employees interact with HR systems.
2. Hiring is about quality, not quantity
Quote: “The talent shortage isn’t about numbers — it’s about skills alignment.”
Why it matters: Recruiting strategies must focus on quality hires and internal mobility, not endless sourcing.
Action: Build “talent intelligence” dashboards that connect hiring with performance.
Added insight: Kathi Enderes (Josh Bersin Company) challenged, “How can we make every person count more?” emphasizing outcomes over sheer headcount.
3. Assessments go AI-first
Discovery: Platforms like SHL, Pymetrics, etc., are using adaptive AI-driven assessments to personalize difficulty and reduce bias.
Why it matters: Fairness and scalability in hiring depend on intelligent assessment tools.
Action: Replace one-size-fits-all assessments with adaptive, feedback-driven models.
Quote: Robin Barbacane (Rackspace) said, “When you first create your AI tool, talk to it like an intern,” highlighting practical ways to integrate AI safely.
4. Internal mobility is the new sourcing strategy
Stat: 65% of companies invest in improving manager and employee mobility experiences (Aptitude Research).
Why it matters: Moving people internally is more cost-effective and improves morale.
Action: Create internal job boards and mobility marketplaces.
Quote: Josh Gosliner (SAP) reminded us, “HR data can’t live in silos anymore,” reinforcing the need for connected internal talent strategies.
Theme 2: Skills as the New Currency
5. Skills-based strategies dominate HR agendas
Stat: 58% of companies prioritize skills-based hiring and internal mobility.
Discovery: Platforms like Eightfold, Gloat, and SkyHive showcased live skills graphs linking learning to career paths.
Action: Start with a skills baseline; Platforms like Tekstac make this easier by capturing learning performance data that reflects actual skill growth, helping organizations keep their skills business aligned.
Quote: Heidi Barnett (isolved, Talent Acquisition) advised, “Think about complementary skills and help describe who a job would be perfect for.”
6. Career pathing becomes skills-driven
Quote: Madeline Laurano noted, “Employees don’t want a static career ladder—they want dynamic growth journeys based on skills.”
Why it matters: Retention improves when employees see a personalized path forward.
Action: Use platforms that visualize “if you learn X, you can move into Y role.”
7. Pay transparency and skills-linked compensation rise
Discovery: Vendors like Visier, CompXL link pay to skills, not just job titles.
Why it matters: It’s a fairness and DEI issue—and reduces bias in compensation.
Action: Explore skills-based compensation frameworks.
Quote: Heather Kruger (Salary.com) reminded, “Compensation is the foundation—organizations won’t get to higher-order culture dynamics if they don’t get the foundation right.”
Theme 3: Learning & Development Reimagined
8. AI-personalized learning becomes default
Discovery: Platforms like Tekstac, Cornerstone, and Docebo embed adaptive learning journeys that adjust pacing, difficulty, and content.
Why it matters: Personalized learning improves retention, satisfaction, and outcomes.
Action: Shift toward adaptive learning paths tailored to performance and career goals.
Quote: Sandra Loughlin, PhD observed, “Real learning happens in practice, feedback, and flow—not just through structured content.”
9. Skills verification is critical
Discovery: Tools like Degreed, Credly, and blockchain-based platforms offer verifiable skill credentials.
Why it matters: Employers want proof of capability, not just course completion.
Action: Incorporate verifiable assessments into programs.
10. ROI in L&D is finally measurable
One of the panelists quoted: “The ROI black hole is closing AI gives us real business outcome tracking.”
Why it matters: Learning is expected to drive promotion, performance, and retention.
Action: Tie learning outcomes to business metrics.
Quote: Jason Averbook emphasized, “In 2025-26, HR needs a reset. Otherwise, we’re putting digital lipstick on an analog pig.”
Theme 4: Employee Experience & Wellbeing
11. EX platforms become central hubs
Discovery: ServiceNow, Qualtrics, and Microsoft integrate surveys, workflows, and learning.
Why it matters: Employees expect consumer-grade experiences at work.
Action: Invest in EX platforms that unify communications, HR tasks, and career tools.
12. Managers are the new power users
Gartner found that among HR decision-makers, leader and manager development remains the number one priority.
Action: Give managers AI copilots for feedback, coaching, and visibility.
Quote: Bill Pelster, Amber Grewal, and Jaclyn Zhuang shared that managers may lead both people and digital agents, emphasizing hybrid leadership skills.
13. Mental health tech grows mainstream
Discovery: Vendors like Modern Health and Spring Health integrate AI for personalized well-being nudges.
Why it matters: Burnout is a top turnover driver.
Action: Embed well-being into daily workflows.
Quote: Ami Graves said, “Without trust and strong leadership skills in our companies, the technology and AI implementations that we want to implement will fail.”
Theme 5: HR Strategy & Compliance
14. Payroll innovation is back
Discovery: ADP and CloudPay offer real-time pay and AI-driven anomaly detection.
Why it matters: Payroll errors erode trust quickly.
Action: Evaluate tools for speed, fairness, and reliability.
Quote: Pim Altena (Remote) warned, “Trust has a timestamp,” highlighting the link between accuracy and credibility.
15. Trust is the new HR currency
Quote: Josh Bersin emphasized, “Without trust, none of this tech matters.”
Action: Communicate openly about AI and data usage.
16. HR Tech spend is accelerating
Stat: 75% of companies plan to increase HR tech budgets.
Action: Build a strong ROI narrative.
17. Vendors consolidate, but innovation thrives
Discovery: Big HR tech players are expanding fast: Workday acquired Sana, Deel bought Assemble, Paychex snapped up Paycor, Dayforce went private with Thoma Bravo, and HiBob added Pento and Mosaic—while startups keep innovating in niche areas like payroll, AI, and skills taxonomies.
Action: Pilot with smaller players when innovation matters.
Theme 6: GenAI & The Future of Work
18. GenAI moves from hype to workflows
Discovery: Workday, Phenom, and Eightfold showcased enterprise-ready GenAI features.
Why it matters: 64% of HR leaders see GenAI as essential.
Action: Start with low-risk, high-impact areas.
Quote: Nickle LaMoreaux (IBM) said, “It’s HR’s moment in the sun,” urging leaders to seize AI opportunity proactively.
19. Responsible AI is the competitive advantage
Quote: Josh Bersin: “Transparency, bias management, and trust will define which vendors win.”
Action: Audit AI explainability.
20. From chatbots to copilots
Discovery: Microsoft Copilot in Viva, Workday’s AI agent features.
Action: Train teams to collaborate with AI as a partner.
Quote: Kyle Forrest emphasized, “You can’t slap AI solutions on top of existing processes,” underlining the need for integration.
Theme 7: The Future of HR Leadership
21. HR leaders as transformation architects
Action: Upskill HR teams on data literacy, AI fluency, change management.
Quote: Patrick Leddin, PhD, asked, “Do I move towards the change, or do I move towards stability?”—guiding leaders to embrace uncertainty.
22. DEI strategies shift from programs to platforms
Discovery: Textio, Unitive, and certain ATS platforms integrate inclusive language and bias detection.
Action: Audit tools for bias.
23. Hybrid work tech stabilizes
Discovery: Microsoft, Zoom, Slack show hybrid tools as core utility.
Action: Invest in tech that supports hybrid collaboration.
24. Data privacy becomes HR’s responsibility
Action: Collaborate with legal and IT; secure sensitive employee data.
25. Employees expect skills transparency
Discovery: Platforms show employees their skill gaps and potential career paths.
Action: Give employees access to their own skills data.
26. HR must lead, not follow
Quote: Josh Bersin: “This is HR’s time. Don’t wait for tech vendors to define the future — build it yourself.”
Why it matters: Being proactive shapes culture, tools, and strategy.
Quote: Sarah Hodges (UKG) added, “HR tech is the bridge between ideas and outcomes,” reinforcing the strategic impact of HR.
Turning HR Insights into Action
At Tekstac, we see HR Tech 2026 as more than an event; it’s a reflection of how innovation, skills, and strategy are converging. And that’s exactly where our focus lies. The conference brought together industry’s best minds, covering HR insights, innovations, and technology to help organizations stay ahead of change and build the future-ready workforce of tomorrow.
FAQs on HR Insights
1. What are HR Insights?
HR insights are data-driven, strategic understandings derived from workforce, talent, and performance data that help organizations improve hiring, learning, engagement, productivity, and business outcomes.
2. What are the 7 pillars of HR?
The 7 pillars of HR include talent acquisition, learning and development, performance management, employee engagement, compensation and benefits, workforce planning, and HR analytics, all working together to drive organizational growth.
3. What are the 4 types of HR analytics?
The four types of HR analytics are descriptive (what happened), diagnostic (why it happened), predictive (what will happen), and prescriptive (what should be done), enabling data-driven HR strategies.
4. How do HR insights impact business strategy?
HR insights help organizations align talent, skills, and leadership with business goals, enabling faster decision-making, improved productivity, and sustainable workforce transformation.
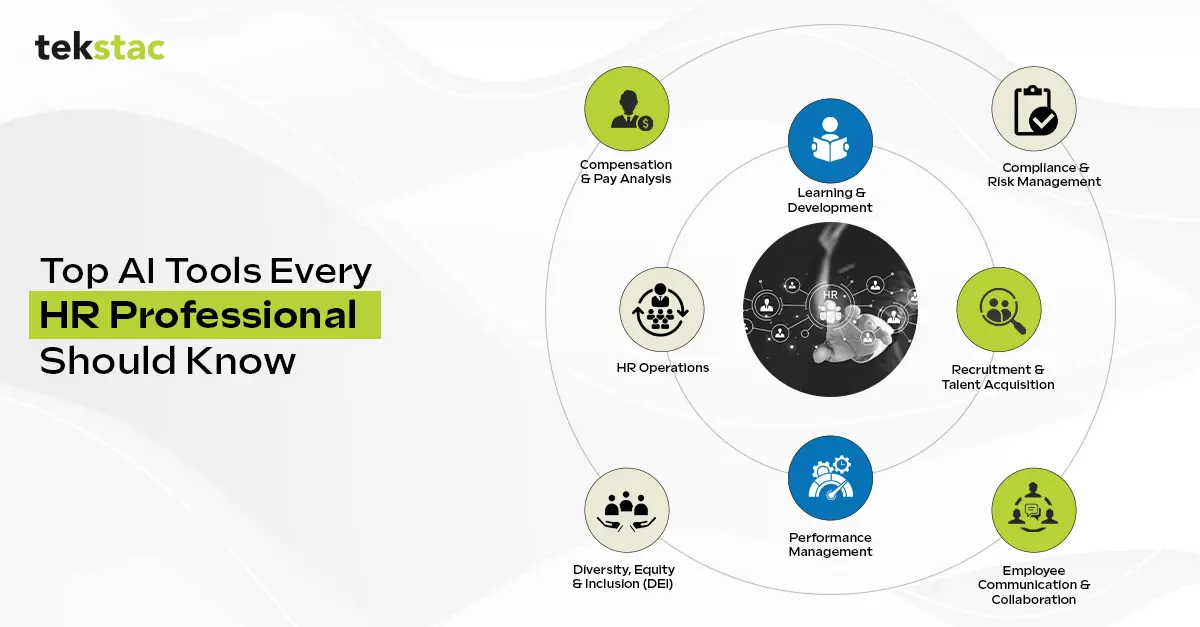
26 AI Tools That Will Reshape HR Tech in 2026
Selecting the right HR Tech tool is crucial to optimizing processes and achieving organizational goals. With countless options available, choosing the best tools requires careful consideration.
Here’s your ultimate list of 26 AI tools that will help you streamline HR processes, boost employee experience, and drive measurable business impact.
Let’s dive in, category by category.
Comparison of 26 Leading AI Tools for HR Automation
| Category | Company Name | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Learning & Development | Tekstac | Custom pricing |
| Degreed | Custom pricing | |
| Fuse Universal | Starts at $25,000 annually | |
| Recruitment & Talent Acquisition | LinkedIn Talent Insights | $170/month (single license); $270/month per license (licenses 2–5); $1,680/year (single license); $2,670/year (licenses 2–5) |
| Pymetrics | Starts at $10,000 annually | |
| SeekOut | Basic: $499/month; Pro: $999/month; Enterprise: $1,999/month | |
| HireVue | Entry-level plans start at $39/month | |
| Performance Management | Effy AI | Free for up to 5 members; $6–$8 per seat/month for employee reviews; $3–$7 per seat/month for performance and 360° reviews |
| ClearCompany | Custom pricing | |
| HR Operations | Leena AI | Custom pricing |
| BambooHR | Starts at $99/month for 12 users; additional users at $8.25/user/month | |
| Praisidio | Custom pricing | |
| Lattice | Starts at $11/user/month; custom pricing for larger organizations | |
| Monday.com | Basic: $49/month for 10 users; Standard: $79/month; Pro: $119/month; Enterprise: custom pricing | |
| Zapier | Free plan available; paid plans start at $19.99/month | |
| UiPath | Custom pricing | |
| Compliance & Risk Management | HR Acuity | Custom pricing |
| Compliance.ai | Custom pricing | |
| BrightMine | Custom pricing | |
| Employee Communication & Collaboration | Workday | Custom pricing |
| Slack | Free plan available; paid plans start at $6.67/user/month | |
| Trello | Free plan available; paid plans start at $5/user/month | |
| Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI) | Asana | Free plan available; paid plans start at $10.99/user/month |
| Diversio | Custom pricing | |
| Blendoor | Custom pricing | |
| Compensation & Pay Analysis | PayScale | Custom pricing |
AI Tools for Learning & Development
1. Tekstac
Best For: Organizations seeking verifiable upskilling, measurable ROI, and business-aligned learning outcomes.
Standout Feature: Dual-layered assessments (auto + video with AI proctoring)
How it Works
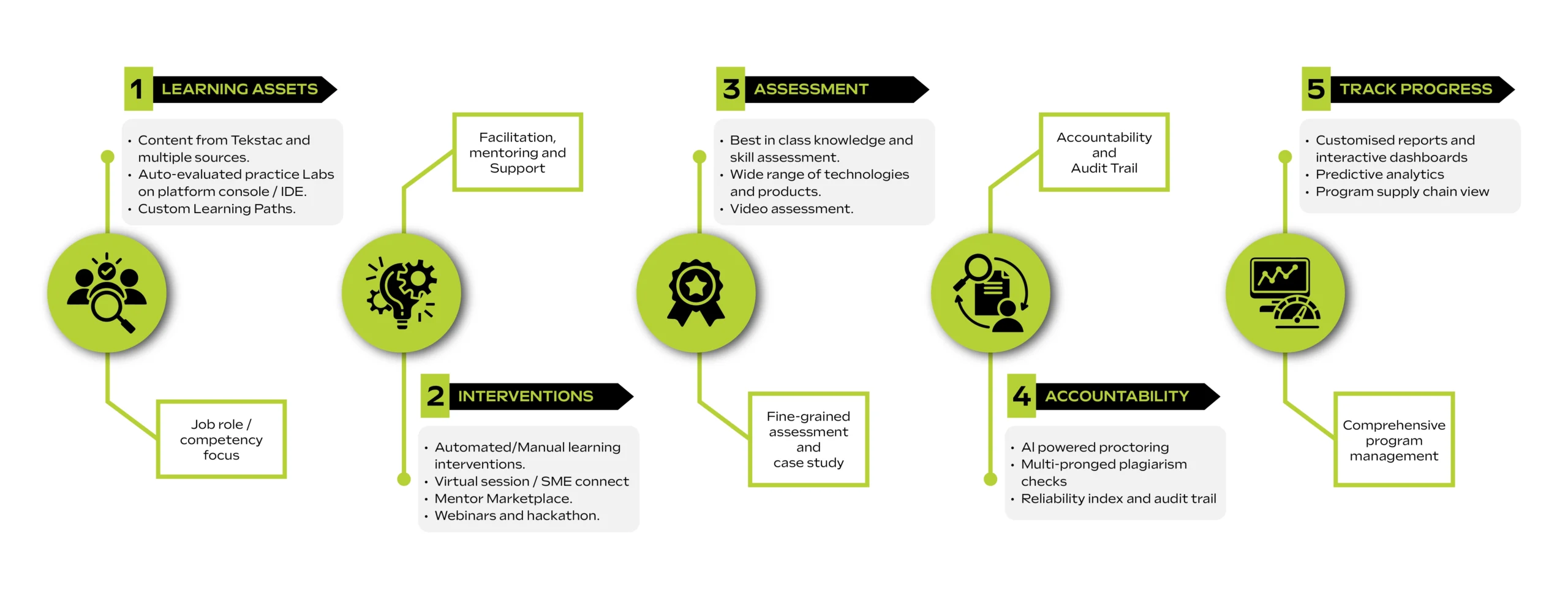
Tekstac Features:
- 360-degree platform with measurable ROI
- 500+ customizable, role-aligned learning paths
- Auto-evaluated coding labs with instant grading
- Mentor marketplace with structured rubric feedback
- Gamified experience with XP points, badges, and leaderboards
- AI-powered personalization & live dashboards
- Enterprise-grade security & compliance
- Data-driven skills insights
2. Degreed
Best For: Organizations that want to centralize learning, upskilling, and continuous education
Standout Feature: Highly flexible learning pathways and personalized content recommendations.
Features:
- Personalized learning pathways combining internal & external content
- Aggregation of diverse learning resources (books, podcasts, courses)
- Easy-to-use UI & third-party integration
3. Fuse Universal
Best For: Organizations and L&D teams building a culture of continuous learning.
Standout Feature: AI-powered personalized learning journeys + social learning.
Features:
- AI recommendations based on role, skills, interests, goals
- Unified content hub (internal, external, user-generated)
- Microlearning & curated modules for busy schedules
AI Tools for Recruitment & Talent Acquisition
4. LinkedIn Talent Insights
Best For: HR leaders, recruiters, and organizations seeking data-driven workforce planning
Standout Feature: Real-time insights on talent availability and workforce trends
Features:
- Talent Pool & Company Reports
- Competitive Benchmarking
- Skills & Location Mapping
5. Pymetrics
Best For: Talent acquisition teams looking for bias-free candidate evaluation
Standout Feature: Neuroscience-based games assessing cognitive & emotional traits
Features:
- AI-driven gamified assessments
- Candidate profiling beyond resumes
6. SeekOut
Best For: Companies prioritizing diversity hiring
Standout Feature: Advanced AI filters for diversity & real-time skills analysis
Features:
- AI-powered candidate sourcing
- Searches public databases & networks
- Advanced diversity filters
7. HireVue
Best For: High-volume recruitment across industries
Standout Feature: AI insights into candidate personality & cultural fit
Features:
- AI-powered video interviewing
- Analyzes facial expressions, tone, word choice
- Customizable evaluation metrics
AI Tools for Performance Management
8. Effy AI
Best For: Growing companies streamlining performance reviews
Standout Feature: Complete 360-degree review in just 60 seconds
Features:
- Quick setup for reviews
- Automates questionnaires & participant matching
- AI-generated reports & Slack integration
9. ClearCompany
Best For: Companies fostering continuous improvement & data-driven performance
Standout Feature: AI-powered alignment of individual & team goals
Features:
- Goal tracking & 360-degree feedback
- Performance analytics & insights
AI Tools for HR Operations & Automation
10. Leena AI
Best For: Large/distributed enterprises with high HR query volumes
Standout Feature: “Siri for employees” – instant query resolution
Features:
- 24/7 AI-powered HR assistant
- Integrates with HRIS like Workday & SAP
- Automates FAQ responses
11. BambooHR
Best For: Small to mid-sized companies seeking efficient HR automation
Standout Feature: End-to-end AI automation of HR workflows
Features:
- Employee records & payroll automation
- Benefits tracking & HR workflow automation
12. Praisidio
Best For: HR leaders seeking insights to improve recruitment & retention
Standout Feature: AI-driven organizational insights
Features:
- Unified HR database
- Step-by-step HR process assistant
- Integrates with platforms like ADP, Workday, Lattice
13. Lattice
Best For: Organizations with existing HRIS wanting predictive workforce insights
Standout Feature: Context-aware AI Agent for trends, risks, & insights
Features:
- Pattern detection & insights
- Workflow integration & meeting assistant
14. Monday.com
Best For: HR teams automating onboarding, approvals, tasks, & status tracking
Standout Feature: Pre-built automation recipes + deep integrations
Features:
- Workflow automation with pre-set triggers & actions
- Multiple board views (Kanban, Calendar, Gantt)
15. Zapier
Best For: HR teams looking to automate repetitive tasks
Standout Feature: AI-powered “Zaps” for workflow automation
Features:
- Connects apps & reduces manual data entry
- Customizable automation workflows
16. UiPath
Best For: Enterprises with repetitive, large-scale HR/back-office tasks
Standout Feature: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) with AI task execution
Features:
- Builds software robots mimicking human actions
- Integrates with existing systems
AI Tools for Compliance, Risk & HR Governance
17. HR Acuity
Best For: HR/employee relations teams seeking compliant & proactive case management
Standout Feature: AI-driven executive summaries & trend reporting
Features:
- Case management for investigations
- Smart interview question generation
- Multilingual support & analytics
18. Compliance.ai
Best For: Highly regulated industries (finance, healthcare)
Standout Feature: Real-time legal & regulatory AI alerts
Features:
- NLP for regulations
- Tracks legal updates &alerts
19. BrightMine
Best For: Enterprises operating across multiple geographies
Standout Feature: AI Assist with access to 23,000+ HR resources
Features:
- Automates compliance tasks
- Provides AI-powered HR resources
AI Tools for Employee Communication & Collaboration
20. Workday
Best For: Organizations modernizing HR with AI efficiency & inclusivity
Standout Feature: Holistic AI integration across all HR functions
Features:
- Personalized learning & skill development
- Employee engagement & sentiment analysis
- AI HR support chatbots
21. Slack
Best For: Remote-first & hybrid teams
Standout Feature: AI-generated conversation recaps
Features:
- AI-powered personalized search
- Summarizes conversations & missed messages
22. Trello
Best For: HR teams managing projects & onboarding tasks
Standout Feature: AI-powered task automation with visual workflow boards
Features:
- AI-powered project management
- Task assignment & tracking
23. Asana
Best For: Teams improving project execution & productivity
Standout Feature: AI converts notes into actionable tasks & predicts optimal timelines
Features:
- Intelligent task management
- NLP-based note-to-task automation
- Workflow bottleneck detection
AI Tools for Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI)
24. Diversio
Best For: Organizations improving DEI across teams & geographies
Standout Feature: Real-time DEI metric tracking with AI recommendations
Features:
- AI-driven DEI data tracking
- Surveys & targeted questions
25. Blendoor
Best For: Organizations committed to equitable recruiting & bias reduction
Standout Feature: Anonymized hiring filters + equity-focused analytics
Features:
- Candidate evaluation without demographic identifiers
- Transparent filters & analytics
AI Tools for Compensation, Pay Analysis & Workforce Planning
26. PayScale
Best For: Organizations seeking competitive & equitable compensation strategies
Standout Feature: Real-time market data for informed salary decisions
Features:
- Advanced search & survey participation
- Data transparency & validation
The Impact of AI Tools on Modern HR Strategy
With the 26 AI tools outlined above, HR leaders can identify solutions that align with their specific needs, whether it’s boosting employee engagement, fostering continuous learning, reducing bias in hiring, or optimizing workforce planning.
Among these, Tekstac stands out in HR Tech for its dual-layered assessments, AI-powered personalization, and data-driven skills insights, making it ideal for organizations that want measurable ROI from learning programs, verifiable upskilling, and business-aligned outcomes.
The Learning Shift in Action: How Companies Win with L&D Transformation
In boardrooms and on the front lines, a quiet revolution is underway.
The world of corporate Learning & Development (L&D), once a predictable function of compliance checklists and scheduled seminars, is undergoing a seismic shift. The old playbook of delivering training for the sake of coverage is being replaced by a far more ambitious mandate: build capability.
It’s less about pushing content into people’s calendars and more about creating ecosystems where employees are pulled toward growth because they see the direct value in it.
This learning transformation is the heartbeat of The Learning Shift, a new LinkedIn series by Tekstac featuring insights from seasoned L&D leaders. It’s not just an internal shuffle or a passing trend. It’s a strategic imperative for any organization aiming to thrive in an era defined by disruption, rapid technological change, and shifting workforce expectations.
The consensus from the leaders we spoke to is unmistakable: L&D is moving from a support service to the engine room of business agility and resilience.
Learning Shift Mandate: From Training Provider to Strategic Capability Builder
The role of L&D has fundamentally expanded.
As DJ Jaeger, Senior Training Manager at Akamai Technologies, puts it: “L&D is becoming a strategic driver of organizational capability, not just a service provider.” The expectation has shifted from simply “doing more with less” to “delivering greater impact with less.”
That’s not just semantics; it’s a mindset shift. It means moving beyond measuring success by course completions and attendance sheets. Instead, the focus is on fostering genuine skills, workforce agility, and adaptability priorities that have firmly landed on the board’s agenda.
But here’s the thing: strategic alignment doesn’t happen by accident.
Meeta Kanhere, a leadership consultant, points out a critical blind spot in many organizations: a lack of clarity on the why behind workplace learning. Before engaging consultants or launching a program, leaders must articulate what success looks like.
Without that clarity, L&D risks operating in a vacuum, designing elegant solutions to problems no one has defined. The most impactful learning strategies emerge when L&D partners with the business to diagnose challenges, define desired outcomes, and co-own the results.
Imagine two scenarios:
- In one, L&D rolls out a new leadership program because “we need more leaders.” The result? Mixed engagement, vague metrics, and little change in behavior.
- On the other hand, L&D starts by asking, “What capabilities will leaders need to take this business through its next phase of growth?” From there, they co-design experiences that directly address those needs. The difference is night and day, and so are the results.
AI as the Co-Pilot: Amplifying Human Potential
No conversation about the future of L&D can ignore Artificial Intelligence.
Its role, however, is widely misunderstood. Santosh Akella, an L&D professional and keynote speaker, frames it perfectly: “AI should be the co-pilot, not the pilot.”
AI’s value lies in the heavy lifting of curating content, identifying skill gaps, and automating time-consuming administrative tasks. DJ Jaeger adds that AI can handle taxonomy management, smart tagging, and even initial learning path creation, freeing L&D professionals to focus on higher-order work: engaging learners, coaching leaders, and shaping culture.
For Aveshkumar Jha, Global Head of Organization Development at Hinduja Global Solutions, the message is blunt: “Stop fearing technology. Embrace it. Befriend it.”
L&D leader Sheena backs this up with data, pointing to research that shows how AI powered adaptive learning can dynamically adjust content based on a learner’s pace, preferences, and performance. That turns skills development from a generic exercise into a deeply personalized growth journey. An employee struggling with a new sales process is automatically recommended targeted simulations and peer-led case studies, while another who’s excelling is served advanced modules and mentoring opportunities. Both are engaged, challenged, and supported at scale.
The Great Shift: From Push to Pull Learning
Perhaps the most profound change in modern learning is the shift from “push” to “pull.” For decades, corporate learning was built on a push model of mandatory modules, compliance checklists, and quarterly workshops. Employees participated because they had to.
But today’s workforce, especially Millennials and Gen Z, learns differently. They expect learning to be on-demand, relevant, and embedded into the flow of work. As Santhosh puts it: “An employee facing a tough client call won’t wait for the next webinar; she’ll find what she needs right now.”

This is pull learning when employees actively seek out knowledge and skills because they see immediate value.
Avesh explains that employees want learning that speaks directly to their current roles, future ambitions, and personal interests. They prefer formats they can consume in short bursts, bite-sized videos, quick simulations, or peer discussion threads.
Sheena’s research shows that microlearning often outperforms traditional training in both engagement and retention. And when it’s integrated into the tools people already use, like Microsoft Teams or Slack, it becomes part of the workday rather than an interruption.
Social learning, too, is gaining ground. Peer-led communities and collaborative forums don’t just distribute knowledge; they strengthen culture and boost application. In fact, Sheena cites data showing that social learning can improve on-the-job application by up to 75%*.
The question for leaders, Santhosh says, must evolve from “How do we make them complete this course?” to “How do we make them want to?”
*According to the 2023 Brandon Hall Group Study.
The Irreplaceable Human Core in a Digital Age
For all the excitement around AI and automation, the human element remains the anchor of impactful learning.
Santhosh reminds us: no algorithm can replace the spark of a great mentor, the resonance of a compelling story, or the thrill of discovery.
Sheena points to psychological safety as a crucial driver of deeper learning. When people feel safe to ask questions, challenge ideas, and admit mistakes without fear of judgment, they engage more fully and innovate more freely.
Avesh adds a deceptively simple truth: learning sticks when it’s fun. Whether through gamified simulations, creative challenges, or interactive storytelling, enjoyment deepens retention.
DJ Jaeger notes that coaching, once reserved for executives, is now being democratized. Everyone, from entry-level employees to mid-career professionals, can benefit from personalized guidance. This doesn’t just accelerate skill development; it reinforces a continuous learning culture where growth is accessible to all.
The Road Ahead: Driving Business Growth Through L&D Transformation
The path forward demands courage, experimentation, and a willingness to lead from the front.
DJ Jaeger cautions leaders against a “wait and see” stance on innovation, especially with AI. The bigger risk, he argues, is being left behind. Early adopters have the advantage of shaping the tools to fit their culture and needs.
Meeta warns against common pitfalls: making decisions driven purely by short-term cost savings, underestimating the importance of sustained sponsorship, and neglecting the creation of internal champions who can carry momentum forward.
In the end, L&D transformation won’t just imply the number of training courses. As DJ Jaeger puts it: “Your legacy isn’t the content you create; it’s the capability you build.”
That’s the real measure of success in the new era of learning: whether your people are more adaptable, more confident, and more capable of taking on tomorrow’s challenges than they were yesterday.
The Learning Shift: What It Means for Your Business
The learning shift is not a memo you send out. It’s a cultural rewire. It’s the difference between a workforce that survives change and one that drives it. And it starts with leaders willing to see L&D not as a cost center, but as the architect of the future.
Tekstac empowers L&D professionals with a 360 degree end to end skilling platform to stay current with rapidly changing technologies. See our mission in action.
This article brings together insights from industry leaders who are shaping the future of learning and development. Below are the voices behind these perspectives—leaders whose experiences across global organizations, startups, and academia offer a rich view of how capability-building is evolving in the GenAI era.
Avesh Jha is Senior Vice President of Global Organizational Development & Performance Management at Hinduja Global Solutions. With 30+ years of global experience, he specializes in leadership development, performance management, and guiding large-scale business transformations.
Sheena Vengiyil is Learning Lead for the India GCC Business at Maximus and a 2024 HR 40 Under 40 honoree. She brings 16 years of expertise in designing impactful learning strategies across global organizations.
DJ Jaeger is Senior Training Manager for Customer Learning and M&A at Akamai Technologies and an adjunct instructor at Portland State University. She focuses on enterprise learning systems, upskilling programs, and inclusive workplace practices.
Meeta Kanhere is Co-Founder of Meraki Leadership Solutions and a seasoned consultant in leadership and organizational development. She works with organizations to build high-performance teams and value-driven cultures.
Santosh Akella is Assistant Manager – L&D at Cognitus and a former president of the Hyderabad Chapter of the Professional Speakers Association India. He is known for creating coaching cultures and designing learning programs that align with business goals.
Top 7 Learning and Development (L&D) Trends for Enterprises in 2026
Discover the 7 learning and development trends for upskilling in 2026, from AI-driven to VR training and continuous learning. Try to stay ahead in that bell curve and succeed in your career!
What Are the Top Learning and Development Trends for 2026?
With growing dependencies on Gen AI, learning & development departments will continuously evolve in 2026. In order to stay relevant in the growing market, it’s imperative to follow the latest trends and be a part of a futuristic workplace.
So, what are the top Learning and Development Trends for 2026?
The leading L&D trends include AI-driven upskilling, hyper-personalized learning paths, microlearning, and data-driven learning strategies.
Read on to deep dive into what’s new in L&D and where it’s all headed.
US Learning & Development Trends: Insights from WEF Report
According to the Future of Jobs Report 2025 by the World Economic Forum, the findings related to the USA show that organizations are taking significant steps to prepare their workforce for the future.
Key observations include:
- 39% of workers (Global: 41%) do not need training by 2030.
- 29% of workers (Global: 29%) would be upskilled in their current role.
- 21% of workers (Global: 19%) would be upskilled and redeployed.
- 11% of workers (Global: 11%) say they would be unlikely to upskill.
- 94% of respondents identified AI and related technologies (e.g., big data, virtual reality, augmented reality) as key drivers of business transformation.
Corporate L&D Trends Shaping Enterprises in 2026
Whether you’re looking to reskill, upskill, or future-proof your workforce, staying aligned with the latest L&D innovations is essential.
Let’s explore the top 7 corporate learning and development trends set to create growth waves in 2026.
- AI-Driven Skill Development for Future-Ready Employees
- Hyper-Personalized Upskilling Method
- Microlearning
- Immersive Learning
- Data-Driven Learning
- Gamification
- Social Learning Platforms

1. AI-Driven Skill Development for Future-Ready Employees
AI or Artificial Intelligence is crucial for skill development. It helps companies to identify gaps and forecast futuristic upskilling requirements.
What we now need in 2026 is Responsible AI adoption. Companies need to design Human+AI approach that enables people to thrive in partnership with AI.
Following this allows IT aspirants to align their knowledge with the current demand for skills and to stay ahead of the bell curve such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cloud computing.
2. Hyper-Personalized Upskilling Method
The corporate L&D Program has shifted towards personalized learning where content is customized based on each learner’s skill, responsibility, and goal in career.
In the coming years, companies will focus on specific skills for each person rather than on predefined roles. It leads to greater agility and fills the skill gaps more easily.
3. Microlearning
As professionals are becoming busier, on-demand upskilling has concise. Microlearning is going to dominate L&D strategies in the coming years. It involves bite-sized content to be learned in minutes, which makes it perfect for IT teams who manage tight schedules.
They can learn quickly and apply at any time level of experience. They are perfect for mobile learning and reinforce knowledge through repetition. Tekstac supports microlearning, allowing learners to get access to training modules anywhere, anytime.
4. Immersive Learning
2026, like this year, will equally advocate continuous learning culture with the power of immersive learning technologies. AR or Augmented Reality and VR or Virtual Reality will reign supreme in 2026 also.
With this, IT professionals can engage in the simulated environment to practice troubleshooting systems and coding and handling any complex projects without the risk of the real world.
5. Data-Driven Learning
With the great pressure of the ROI of training programs, the Learning and Development trends in 2026 have been data-driven. Data analytics is the core of any training these days to optimize and customize training programs based on performance metrics, skill gaps, and learning experiences.
For instance, at Tekstac, trainers collect and analyze information from different sources like learning management systems, performance assessments, and feedback surveys, to learn the areas of improvement. Later the insight is used to customize training content, and progress tracking, and to adjust strategies for real-time upskilling.
6. Gamification
The future of corporate learning mostly relies on engagement metrics. The more engaging the training, the better results. Gamification is more than a buzzword. It’s a powerful tool for engaging employees, driving motivation, and fostering collaboration within teams. Gamified learning in 2026 will include AI, VR and AR in the learning environments, setting new benchmarks in immersive learning experiences.
Hybrid and remote working are the future, and it becomes necessary to create engaging L&D programs for remote teams through gamified eLearning. And who doesn’t enjoy a dynamic, game-based learning experience with a bit of healthy competition?
7. Social Learning Platforms
Social learning methodologies are transforming employee training and development in miraculous ways. Platforms like LinkedIn and internal social platforms within organizations are taking precedence for knowledge sharing and group discussions.
Not only that, incorporating interactive forums within LMS tools helps employees engage in real-time and share insights.
Summary of Learning and Development trends
In a nutshell, the main Learning & Development trends in 2026 will continue to be around AI, employee engagement and continuous learning.
Collaborate with solutions like Tekstac to harness the power of cutting-edge learning platforms and drive success. Because the future of work is in evolving and educating peers for company’s collective growth.
Learn better to work better!
FAQs on L&D Trends
1. Why is continuous learning important in 2026?
Continuous learning helps IT professionals to upskill with the latest technologies and perform well. Upskilling makes them more productive and gives job satisfaction in the long term.
2. What is involved in Learning and Development programs?
AI-driven upskilling, hyper-personalized learning paths, microlearning, and data-driven learning strategies.
3. How do companies implement effective L&D programs?
Companies can hire an L&D platform like Tekstac for workforce upskilling needs, where it provides skill-based continuous training to the talents by equipping them with the right tools and knowledge.
4. Why is AI important in corporate learning and development?
AI helps organizations identify skill gaps, personalize learning paths, and predict future upskilling needs. It enhances learning efficiency and supports real-time progress tracking.











